What is Telemedicine?
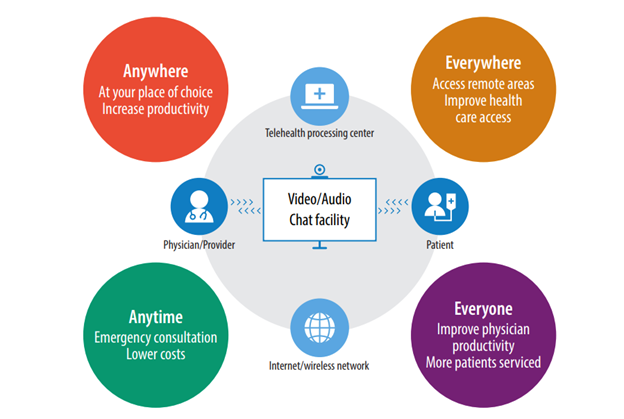
Table of Contents
- Telemedicine vs. Telehealth vs. Telecare
- The Rising Importance of Telemedicine in Healthcare
- Telemedicine Examples
- Telemedicine Requirements
- Telemedicine Is Here to Stay
- Bibliography
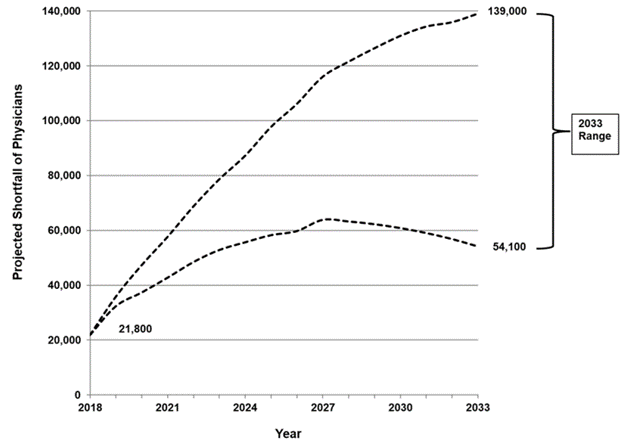
When we try to answer the question, what is telemedicine, we first have to understand that the medical professionals are a scarce resource. From the Bronze age to the modern age, one thing has remained the same. Health practitioners represent rare and prized assets for any group or nation. After all, in modern times, it takes between 10 to 14 years to become a fully licensed medical doctor. Moreover, according to the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC), the United States will face a shortage of about 96,000 physicians by 2033. Other nations will face similar shortages in medical expertise. (The Complexities of Physician Supply and Demand: Projections From 2018 to 2033, 2020).
Thanks to the onset of digital technology and communication systems, it has become possible to take advantage of a physician’s expertise without them being present physically. This is the domain of telemedicine, making expert medical help accessible without the costly expenditure of time and transportation.
No matter if one lives in a sparsely populated region, or if there is a need for emergency expert medical support, telemedicine can deliver that care from a distance. The telecommunication infrastructure needed to make this possible is already widely available using broadband internet.
Telemedicine vs. Telehealth vs. Telecare
Telehealth is an overarching definition covering a broad spectrum of online care relating to diagnoses, monitoring, health education, drug prescriptions, and consultations. Essentially, any healthcare provided, in any format online would fall under this definition.
Telemedicine relates to clinical services offered remotely by licensed medical professionals. This means that a medical doctor could offer care or an examination using telecommunication technology to offset their lack of physical presence.
At the end of the telehealth interaction spectrum lies telecare. It is an automated form of medical monitoring, in which data from vital sign monitoring devices, such as blood pressure cuffs, is relayed to the telecare data center. Thanks to telecare, patients can continue to enjoy the comfort of their home, whilst recording, monitoring and providing their vital sign data to their clinician. This allows for more precise telemedicine sessions further down the line as the clinician will now have access to live data during the call.
In short:
- Telehealth encompasses all healthcare services that can be done remotely.
- Within telehealth, telemedicine relates to the direct interaction with a licensed medical professional for the purpose of diagnosis, education, prescription, and consultation.
- Telecare is a result of telemedicine, in which a doctor gains more detailed information about the patient’s lifestyle, the effect of prescribed drugs, and further medical needs of the patient.
The Rising Importance of Telemedicine in Healthcare

It is no secret that most people prefer not to visit a doctor until it is absolutely necessary. In their minds, people portray such a visit as a special event. With telemedicine, such hesitations are greatly reduced. This is important, as timely interventions and prevention represent key vectors to longevity.
Telemedicine removes the inconvenience of having to wait months to speak with a physician, travel from afar and in most cases is economically beneficial compared to face to face consultations. Patients can access help via:
- Real-time chat via messenger platform
- Video-conferencing
Each stage of communication provides the doctor with a greater pool of detail, as the detail of interaction increases. Therefore, the benefits of telemedicine are numerous for the healthcare system:
- Increased convenience and mental clarity for the patient.
- Early interception of illness, resulting in better treatment outcomes.
- More frequent and casual interactions infers to the patient greater responsibility for their health.
- Doctors can point the patient to web-based illness management programs and local healthcare providers, which are almost always less expensive.
- Reduction of overall healthcare cost by extending the expertise of doctors with little resource expenditure.
- The patient’s record is more easily updated and kept accurate.
As you can see, the advantages of telemedicine are easily apparent when coupled with the will to use the latest telecommunication services, such as web-powered video-streaming, alongside a wide range of telehealth platforms for accessing records, real-time monitoring, and prescription management.
Telemedicine Examples
Chronic conditions provide the best examples of how to successfully deploy and integrate telehealth services. By using automated monitoring equipment that relays data back to Boston’s Partners Healthcare, over 3,000 patients with congestive heart issues were tethered to a telemonitoring software. About 3 – 4 nurses were assigned to groups of 250 patients each.
As a result, this telemedicine program reduced re-admissions by 44%, saving over $10 million.
There are also further examples such as the Kaiser Permanente dermatologists in San Diego, who were able to scrutinize the skin images of hundreds of patients, referring those with worrying signs to physical examinations (Goldberg, 2014).
As a result, the dermatologists now have a telemedicine system in which they can review over 800 patients per month, representing half as much increase as in the previous era of on-site visitation. Needless to say, early interception of skin changes is critical in treating skin cancer, providing another boost in life longevity and convenience, while simultaneously reducing healthcare costs.
In addition to telemedicine, telecare made tremendous progress at the Center for Connected Health (Partners Healthcare), in which patients were provided with wireless prescription bottles. Each bottle was able to signal people when to take their medicine, resulting in a 68% medication intake (Kvedar, 2014).
Telemedicine Requirements
Almost all devices in the last five years, from smartphones to laptops and tablets, are equipped with high-resolution cameras facing the viewer. This makes it extraordinarily easy to establish a telemedicine workflow.
All that is then needed is an internet connection (4G or 5G), and appropriate software (app) to conduct the telemedicine session in either video-form, interactive chat, or a simple email to keep up with updates. All of these details will be worked out by your telemedicine provider.
Even old devices without an integrated camera can be enabled for telemedicine by simply attaching a USB webcam. The technological standard for even the cheapest equipment has drastically increased in recent years, so telemedicine gear has become widely affordable.
Telemedicine Is Here to Stay
As we transition to 5G, there was never a greater momentum to implement telemedicine. The technology to make it happen is cheaper and more effective than ever before. With proper management between tech companies and medical doctors, hospitals can drastically decrease their operating costs and waiting lists, while increasing the convenience and medical efficacy for their patients.
No doubt, with the older generation, some technical education will be needed, but this is a small cost to absorb compared to many positive outcomes.
Bibliography
Ananth, V. (2020). Telehealth: health care industry’s gamechanger? Infosys.
Goldberg, K. (2014). Kaiser Embraces Telemedicine To Improve Access To Dermatology. KPBS.
Kvedar, J. (2014). Connected Health: A Review Of Technologies And Strategies To Improve Patient Care With Telemedicine And Telehealt. Health Affair.
(2020). The Complexities of Physician Supply and Demand: Projections From 2018 to 2033. Association of American Medical Colleges.
